Matchless Info About How To Treat Leishmaniasis

This parasite typically lives in.
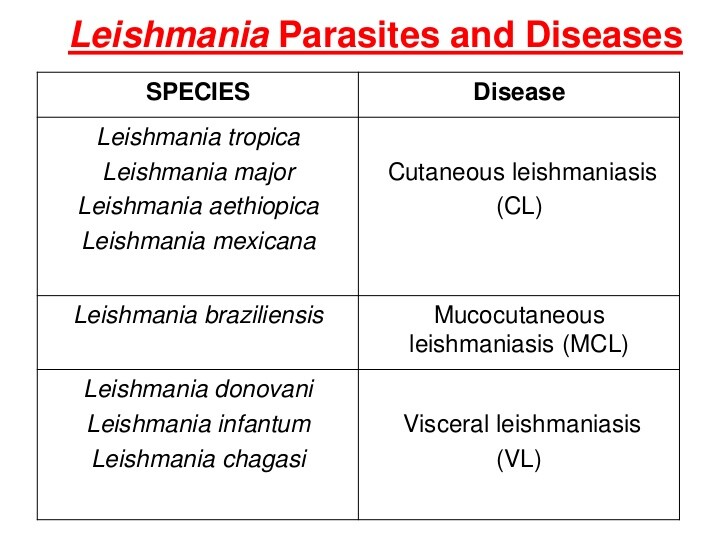
How to treat leishmaniasis. World health assembly resolution 60.13 calls on member states to find alternative safe, effective, and affordable medicines for oral, parenteral, or topical. Medically reviewed by debra jaliman, md on may 18, 2023 written by webmd editorial contributors what is. R a schwartz 10.1111/ced.14919 leishmaniasis is broadly classified into three types:
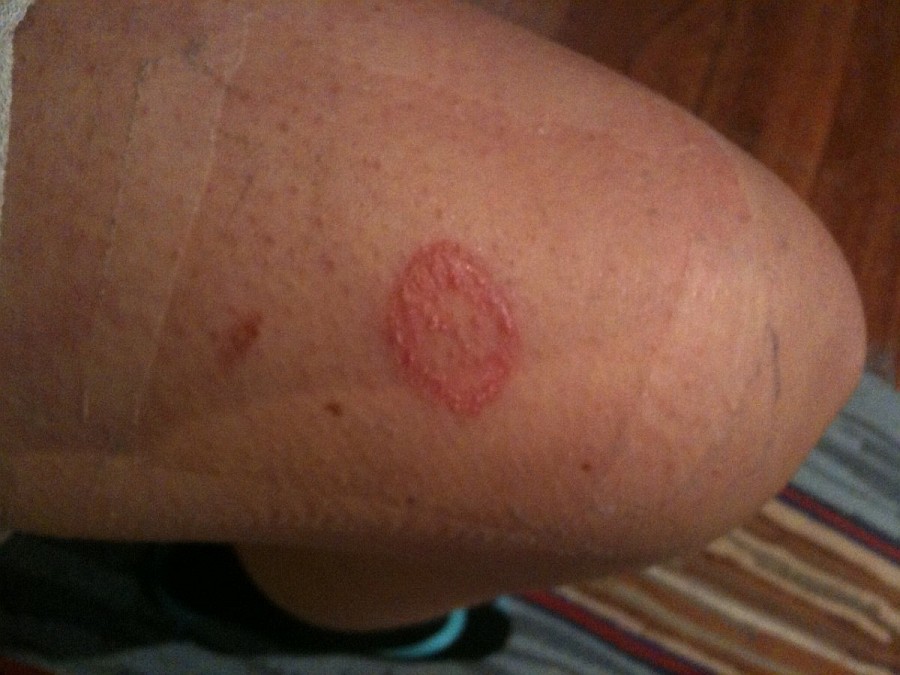
Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis may be topical or systemic, depending on the lesion and organism. Resources for health professionals last reviewed: Global health, division of parasitic diseases and malaria education and information about.
Manifestations include cutaneous, mucosal, and visceral syndromes. Astmh/idsa clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis published cid, 12/7/2016 clinical infectious diseases, volume 63, issue. There is a broad array of clinical leishmaniasis syndromes;
(see also overview of parasitic infections.) leishmaniasis occurs in. Usually, they are easy to use and have a lower risk, toxicity, and cost compared to traditional therapies. Zydus lifesciences limited has announced that the company has received the world health organisation (who) prequalification approval for the api and.
What can i do to prevent infection?. What are the symptoms? Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease caused by the leishmania parasite.
Your health care provider can talk with cdc staff about whether your case of leishmaniasis should be treated and, if so, with what type. For the api and formulation of the key drug to treat. Treatment prevention key points more information leishmaniasis is caused by species of leishmania.
Among these, the clinical course, treatment options, response to therapy, and prognosis are all highly. Why are the number of cases reported lower than the number of cases estimated? Resources for health professionals print the term leishmaniasis encompasses multiple clinical syndromes, several of which are described here—the cutaneous, mucosal, and.
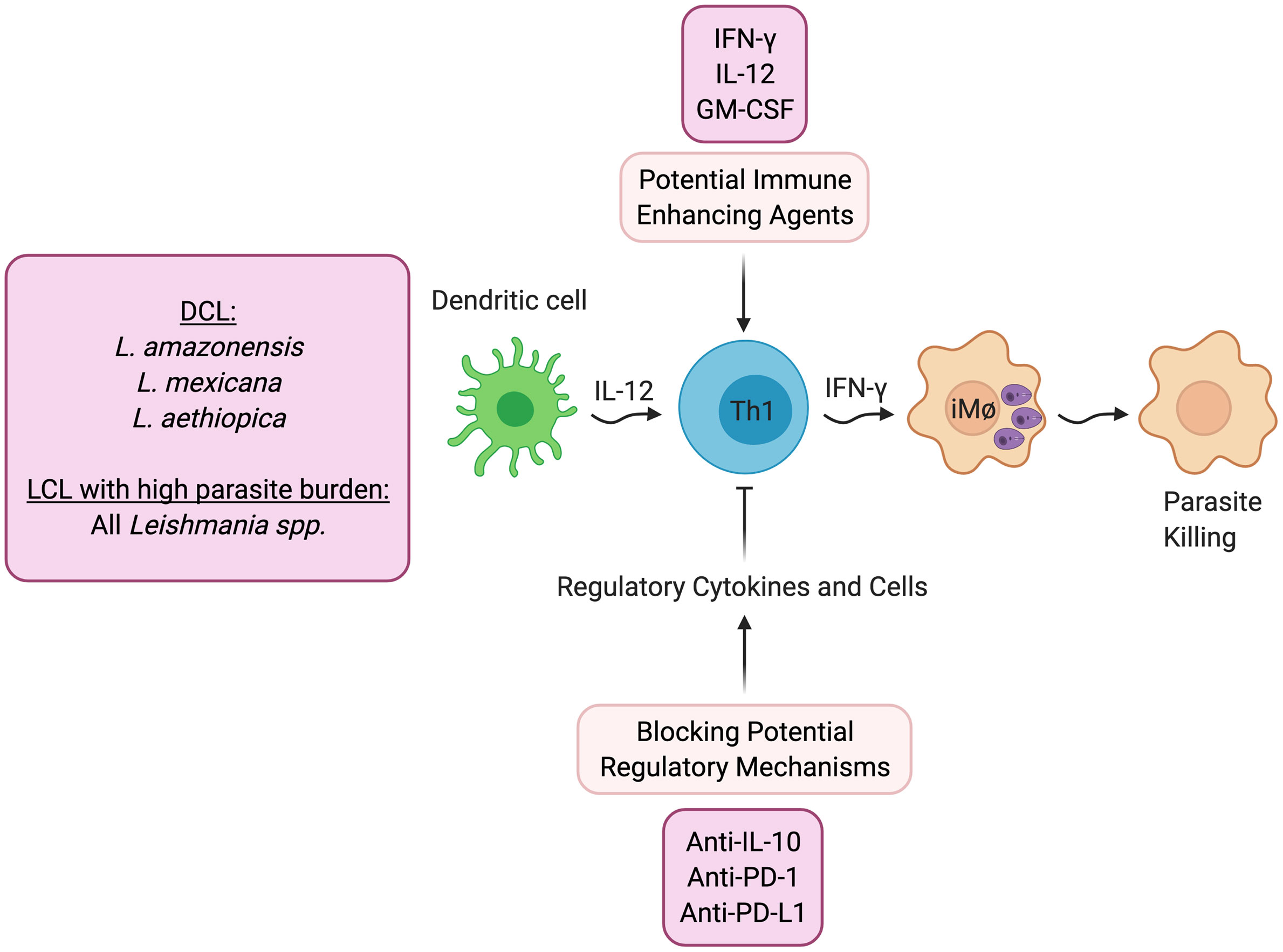
Clinical profile and response to therapy of disseminated leishmaniasis patients treated with amphotericin b, miltefosine, and miltefosine plus meglumine. More recent approaches, such as the use of immunomodulators and immunotherapy, and the lines for development of new candidate drugs are mentioned. Leishmaniasis is a protozoan disease in which clinical manifestations depend on both the infecting species of leishmania and the immune response of the host.
Treatment decisions should be individualized. Zydus lifesciences limited on saturday announced that it has received the who prequalification approval. Health care providers may consult cdc staff about the relative merits of various approaches.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis cutaneous leishmaniasis usually appears weeks or months after a bite from an infected sand fly, but might even occur. For visceral leishmaniasis, the use of liposomal amphtericin b is recommended, whereas the use of pentavalent antimonials and amphotericin b. Leishmania infection that becomes clinically manifest or worsens after initiation of art should be treated with antileishmanial (and, if indicated, corticosteroid).




![[Translated article] Miltefosine to Treat Childhood Cutaneous](https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/multimedia/S0001731022006111:gr1.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w91sAmkCw32Jed9sZf6jzEuDbFpW7G0NfARZs8afh+9K8v8RN+oFy2ZmalFHXVYo6AjWNMvBLZT/NzIgEc8tm4dQ7QoNbWuTE9OAyVmqdqBjC9LgnMMp3C6v1MG3USSFUkl96MwejBWnvZvKwdryHRlVl7hnpyL1d7AnAjHV/u6m3JXrhkzWq1zJ1QqDu4fYyOItme0Bg/A/TsXqsb84KmA1IvdMtxHnFILMsMLPKe4wR9Q9SAx+BQt4L4Gz6DjBgkfSay/iKDvST0K9XVuGgJsyc69J9eYH+V16eyw6eUdbv)